Da click aquí para ver contenido de avanzados
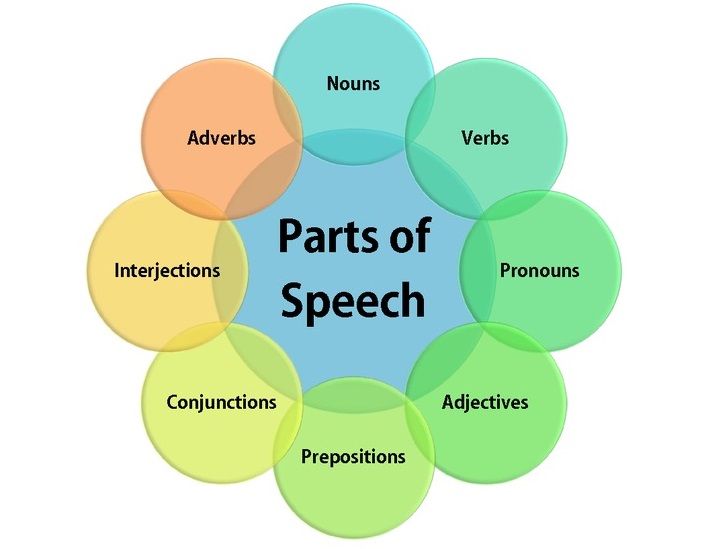
Parts of speech
Conocer las partes de la oración te ayudará bastante a conocer qué función tiene cada una dentro de la oración para entender el por qué llevan una estricta secuencia de sintaxis.

Nouns
Un sustantivo es todo lo que tiene nombre, y se puede clasificar en:
Proper: Specific things like names, cities, countries, brands, etc. (Mariah Carrey, London Bridge, U.S.A, Disney, etc).
Common: General things.(Boy, mom, chocolate, house, etc).
Concrete: Things we can perceive with the 5 senses (flowers, car, cups, dogs,etc).
Abstract: Inmaterial things (love, peace, happiness, etc).
Countable: Everything you can count easily (People, dishes, ctas, etc).
Uncountable: Things we can count unless we have a unit of measure (sugar, water, oil, traffic,etc).
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección

Pronouns
They substitute the noun in order to avoid repeating the same subject again and again. THere are 5 types:
Personal: They are always at the beginning of the sentences (I, you, he, she, it, we, you they).
Object: They come after the verb ans receive th action (Me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them).
Possessive adjectives: They express that an object belongs to someone (My, your, his hers, its, ours, theirs).
Possessive pronouns: They are usually used to compare something and they replace the name of the object already mentioned. (Mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs).
Refelexive Pronouns: They refer that the noun does an action by itself. (Myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves)
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección

Verbs
They express the action tha the noun does. There are some kind of verbs:
Regular: They have an ending in Ed in their past and past participle form.
Irregular: They have different endings in their past or past participle form.
Transitive: It's a verbs that uses a direct object, which shows who or what receives the action in a sentence.
Intransitive:The subject and verb express a complete thought without an object. It's followed by an adverb of manner. (I ran quickly).
Linking: They are verbs that don't show an action but rather describe the subject.
Passive: They are verbs that allow the subject to receive the action rather than to do the action.
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección.

Adverbs
The adverbs that modifies a verb, an adjective and another adbverb.
- Adverbs of manner: Express how something happens (he swims well).
- Adverbs of place: They mention where something happens (They built a house nearby).
- Adverbs of time: Tell us when an action happened (Goldilocks went to the Bears' house yesterday).
- Adverbs of frequency: They express for how long an action happens using frequency words (I always do my homework).
- Adverbs of purpose: They mention describe why something happened. (I was sad because i got a 0 in my homework).
- Adverbs of degree: They refears about the intensity of something. Adverbs of degree are usually placed before the adjective, adverb, or verb that they modify, although there are some exceptions. (The water was extremely cold).
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección

Adjectives
The adjectives are words that describe the noun. There are many different kinf of nouns:
- Attributive adjectives: They are occurring before the noun (The dedicated employee starts early).
- Predicative adjectives: They follow a linking verb, like to be. (The employee is dedicated).
- Comparative adjectives: They increase or decrease the qualitu of a person or an object (Messi is more famous than CR7).
- Superlative adjectives: They mention that only one item is superior from the others. (My mom is the best!)
- Coordinate adjectives: They are two or more adjectives that modify the same noun in a sentence and can be separated by commas or by the conjunction "and.(The plums were cool and delicious.)
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección
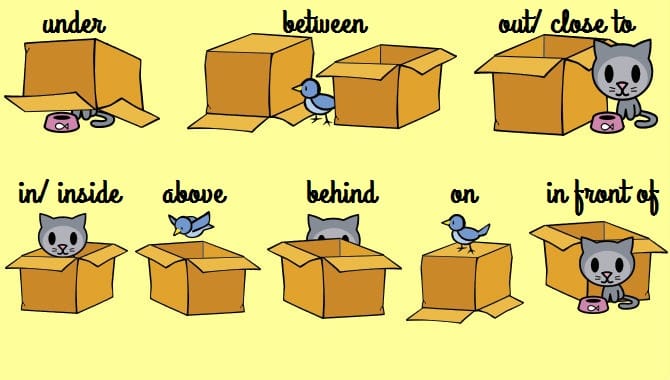
Prepositions
They are used to show the direction of something, the time, the position or location of an object in the sentence, and represent spatial relationships.
Time: Used to show when something is happening (We will be meeting on Friday).
Place: Indicate the place or position of something (Henry hid behind the door).
Direction: Used to denote the direction in which something travels or moves (Jerry jumped into the river to help his sister).
Location: Employed to denote the location of a particular object (Lenny would be staying at his aunt´s place for the weekend).
Prepositions of Spatial Relationship: Used to denote an object's movement away from the source and towards a source (Erick sat leaning against the wall).
Prepositional Phrase: A combination of a preposition and a noun(the object it is affecting (Make sure you fill in all the forms at once).
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección.
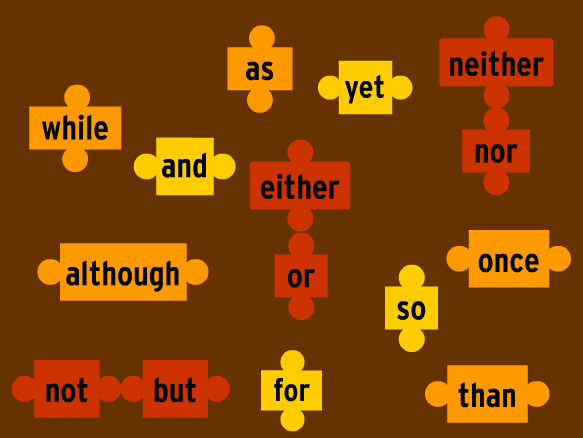
Conjunctions
Conjunctions have an important function because they join other words and phrases together. Without conjunctions, we could only make very, very simple sentences.
Coordinating conjunction: Join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence
(For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So).
Correlative conjunction: pairs of conjunctions that work together. (either/or, neither/nor, and not only/but also).
Subordinating conjunction: Join independent and dependent clauses. (because, since, as, although, though, while, and whereas).
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección.

Interjections
They express emotions such as pleasure, surprise, shock and disgust. Most interjections are just sounds, rather than actual words, and come at the beginning or at the end of what we say.
Meh, I don´t care.
Yuck, I don't like broccoli
Wow! She looks amazing.
Da click al título de esta lección para jugar y repasar la lección.
